Learn in five minutes: An introduction to basic processes in pure water manufacturing and to water treatment technologies
Pure water is used in a wide range of industries. Are you familiar with the technologies used to purify water?
The following introduces the processes of water treatment, from tap water to pure water, as well as the technologies used in purification.
Activated carbon filter treatment
Tap water may appear clear, but it actually contains many impurities. Chlorine, which is added to tap water for sterilization, is a hindrance in water treatment processes.
In general water treatment processes, residual chlorine in tap water is first removed by installing activated carbon filters. Any residual chlorine will cause deterioration in the reverse osmosis (RO) membrane and ion exchange resin installed at later stages, significantly reducing treatment performance. Regular replacement of activated carbon filters can be considered the most important factor in maintaining water quality in water treatment.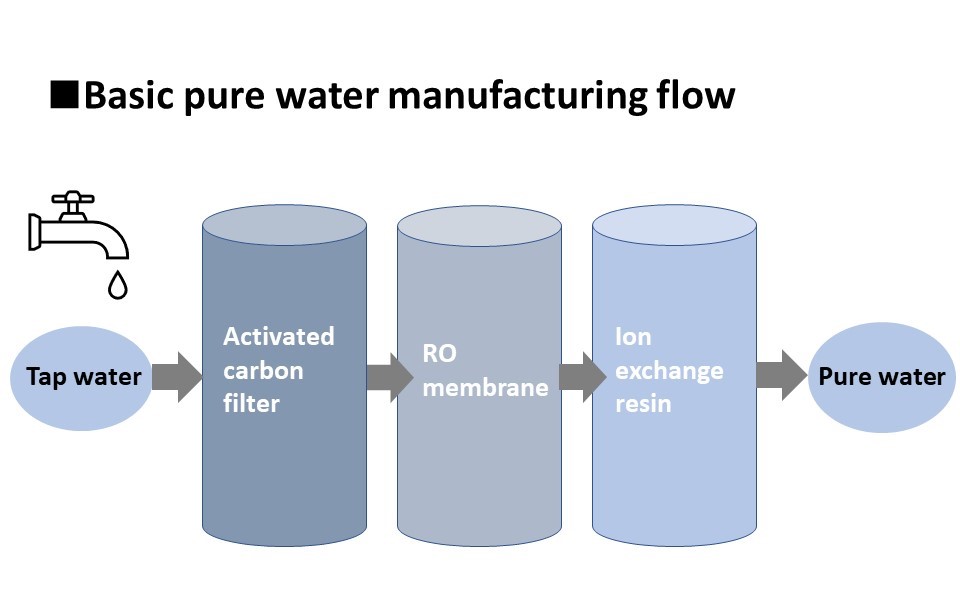
RO membrane treatment
This treatment uses osmotic pressure to filter water through a very fine membrane. An RO membrane can remove over 90% of the ions in water, and can completely remove non-ionized organic matter with high molecular weight and fine particles.
When the RO membrane undergoes chemical deterioration or deterioration over time, the quality of the treated water drops sharply. Moreover, if the membrane becomes clogged with impurities, the inside of the tubing will be subjected to high pressure and the amount of treated water will decrease sharply. The removed impurities are concentrated and are discarded in wastewater.
Ion exchange treatment
Ion-exchange resin is used to chemically remove ions from water. Ion-exchange resin consists of resin beads of less than 1 mm in diameter, with ion exchange functional groups inside.
The ion exchange functional groups contain hydrogen ions (H+) or hydroxide ions (OH-), and are able to exchange these in place of sodium ions (Na+) and chloride ions (Cl-) in water.
This phenomenon is called “ion exchange.”
The technology is commonly used in water treatment as it yields large amounts of treated water easily and for little energy. At the same time, the amount that can be processed is limited. In a saturated state in which all ion exchange functional groups have been exchanged, water treatment is no longer possible. When the resin has become saturated, it must be replaced by new resin or regenerated using acid or alkali.
Summary
The above introduced basic processes in pure water manufacturing and water treatment technologies.
- Activated carbon treatment
- RO treatment
- Ion exchange treatment
If you have any concerns about your water purifier, questions about water, requests for columns, or anything else, we welcome your inquiries here. We look forward to hearing from you!



